1. The names of the various parts of a turning tool
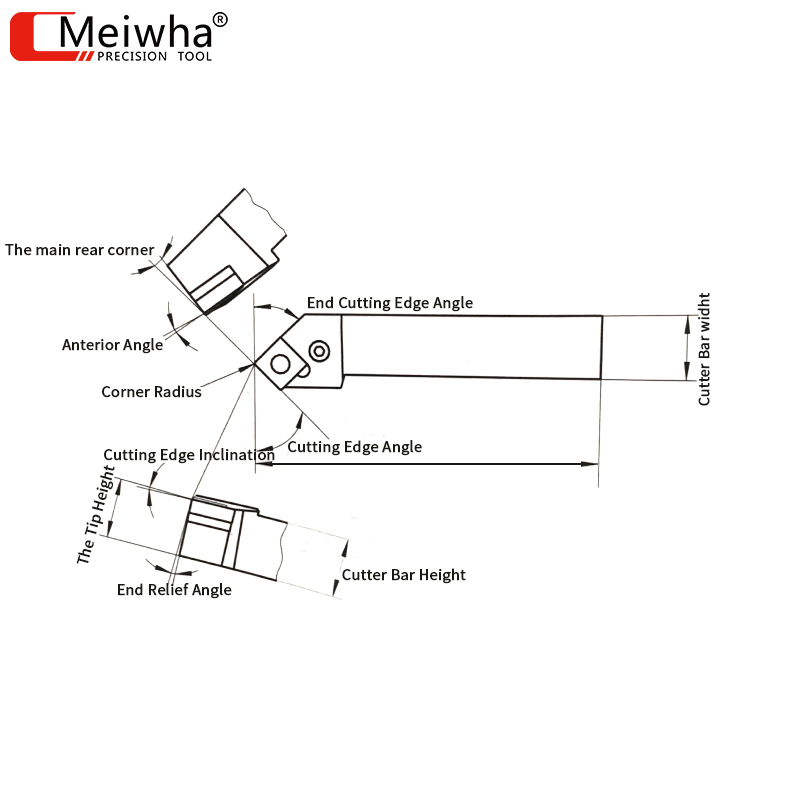
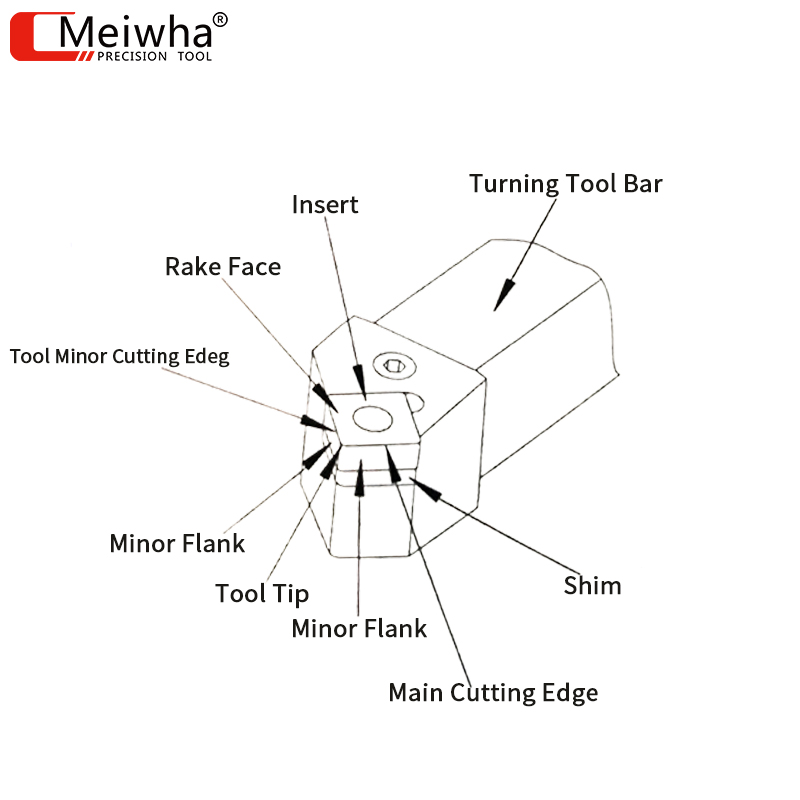
2. The influence of the front angle
An increase in the rake angle makes the cutting edge sharper, reducing the resistance of chip ejection, lowering friction, and minimizing cutting deformation. As a result, the cutting force and cutting power are reduced, the cutting temperature is lower, the tool wear is less, and the surface quality of the processed part is higher. However, an excessively large rake angle reduces the rigidity and strength of the tool, making it difficult for heat to dissipate. This leads to severe tool wear and damage, and a shorter tool life. When determining the rake angle of the tool, it should be selected based on the processing conditions.
| Value | Specific Circumstance |
| Small Anterior Angle | Processing brittle materials and hard materials; Rough machining and intermittent cutting. |
| Big Anterior Angle | Processing plastic and soft materials; Finish machining. |
3. The influence of the rear angle
The main function of the rear angle during processing is to reduce the friction between the rear face of the cutting tool and the processing surface. When the front angle is fixed, an increase in the rear angle can enhance the sharpness of the cutting edge, reduce the cutting force, and decrease the friction. As a result, the quality of the processed surface is high. However, an excessively large rear angle reduces the strength of the cutting edge, leads to poor heat dissipation conditions, and causes a large amount of wear, as the tool life is shortened. The principle for choosing the rear angle is: in cases where the friction is not severe, a smaller rear angle should be selected.
| Value | Specific Circumstance |
| Small Rear Angle | During the rough processing, in order to enhance the strength of the cutting tip; Processing brittle materials and hard materials. |
| Big Rear Angle | During the finishing process, in order to reduce friction; Processing materials that are prone to forming a hardening layer. |
4. The role of the edge inclination angle
The positive or negative value of the rake angle determines the direction of chip removal, and also affects the strength of the cutting tip and its impact resistance.
As shown in Figure 1-1, when the edge inclination is negative, that is, the tool tip is at the lowest point relative to the bottom plane of the turning tool, the chip flows towards the machined surface of the workpiece.
As shown in Figure 1-2, when the edge inclination angle is positive, that is, the tool tip is at the highest point relative to the bottom plane of the cutting force, the chip flows towards the unprocessed surface of the workpiece.
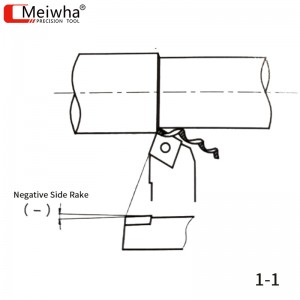
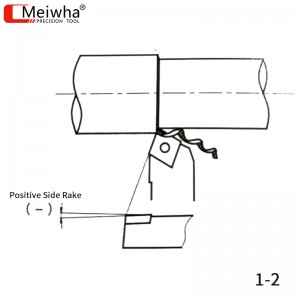
The change in the edge inclination can also affect the strength and impact resistance of the tool tip. When the edge inclination is negative, the tool tip is at the lowest point of the cutting edge. When the cutting edge enters the workpiece, the entry point is on the cutting edge or the front tool face, protecting the tool tip from impact and enhancing its strength. Generally, for large rake angle tools, a negative edge inclination is usually selected, which can not only enhance the strength of the tool tip but also avoid the impact caused when the tool tip enters.
Post time: Jul-30-2025






