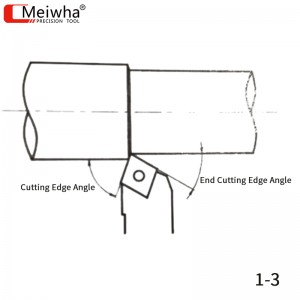
5. The influence of the main cutting edge angle
Reducing the main deflection angle can enhance the strength of the cutting tool, improve the heat dissipation conditions, and result in a smaller surface roughness during processing. This is because when the main deflection angle is small, the cutting width is longer, so the force per unit length of the cutting edge is relatively small. Additionally, reducing the main deflection angle can also increase the lifespan of the cutting tool.
Generally, when turning slender shafts or stepped shafts, a 90° main rake angle is selected; when turning the outer circle, end face and chamfer, a 45° main rake angle is chosen. Increasing the main rake angle reduces the radial component force, makes the cutting process stable, increases the cutting thickness, and improves the chip-breaking performance.
| Value | Specific Circumstance |
| Small Edge Angle | Materials with high strength, high hardness and a hardened surface layer |
| Big Edge Angle | When the rigidity of the machine tool is insufficient |
6. The influence of the secondary angle
The secondary angle is the main factor affecting surface roughness, and its size also affects the strength of the cutting tool. A too small secondary angle will increase the friction between the secondary flank and the already processed surface, causing vibration.
The principle for choosing the secondary angle is that in rough machining or under conditions that do not affect friction and do not cause vibration, a smaller secondary angle should be selected; in finish machining, a larger secondary angle can be chosen.
7. Corner Radius
The radius of the tool tip arc has a significant impact on the strength of the tool tip and the roughness of the machined surface.
A larger tool tip arc radius leads to an increase in the strength of the cutting edge, and the wear on the front and rear cutting surfaces of the tool can be reduced to a certain extent. However, when the tool tip arc radius is too large, the radial cutting force increases, which can cause vibration and affect the machining accuracy and the surface roughness of the workpiece.
| Value | Specific Circumstance |
| Small Corner Radius | Fine processing of shallow cuts; Processing slender shaft-type parts; When the rigidity of the machine tool is insufficient. |
| Big Corner Radius | Rough processing stage; Processing hard materials and performing intermittent cutting operations; When the machine tool has good rigidity. |
Post time: Jul-30-2025






